Despite transitioning from the International Space Station (ISS) to commercially owned space destinations, NASA’s goal remains the same. The space agency says they are still dedicated to scientific developments that benefit humanity. This includes educational and technological developments while also supporting deep space exploration to the Moon and Mars.
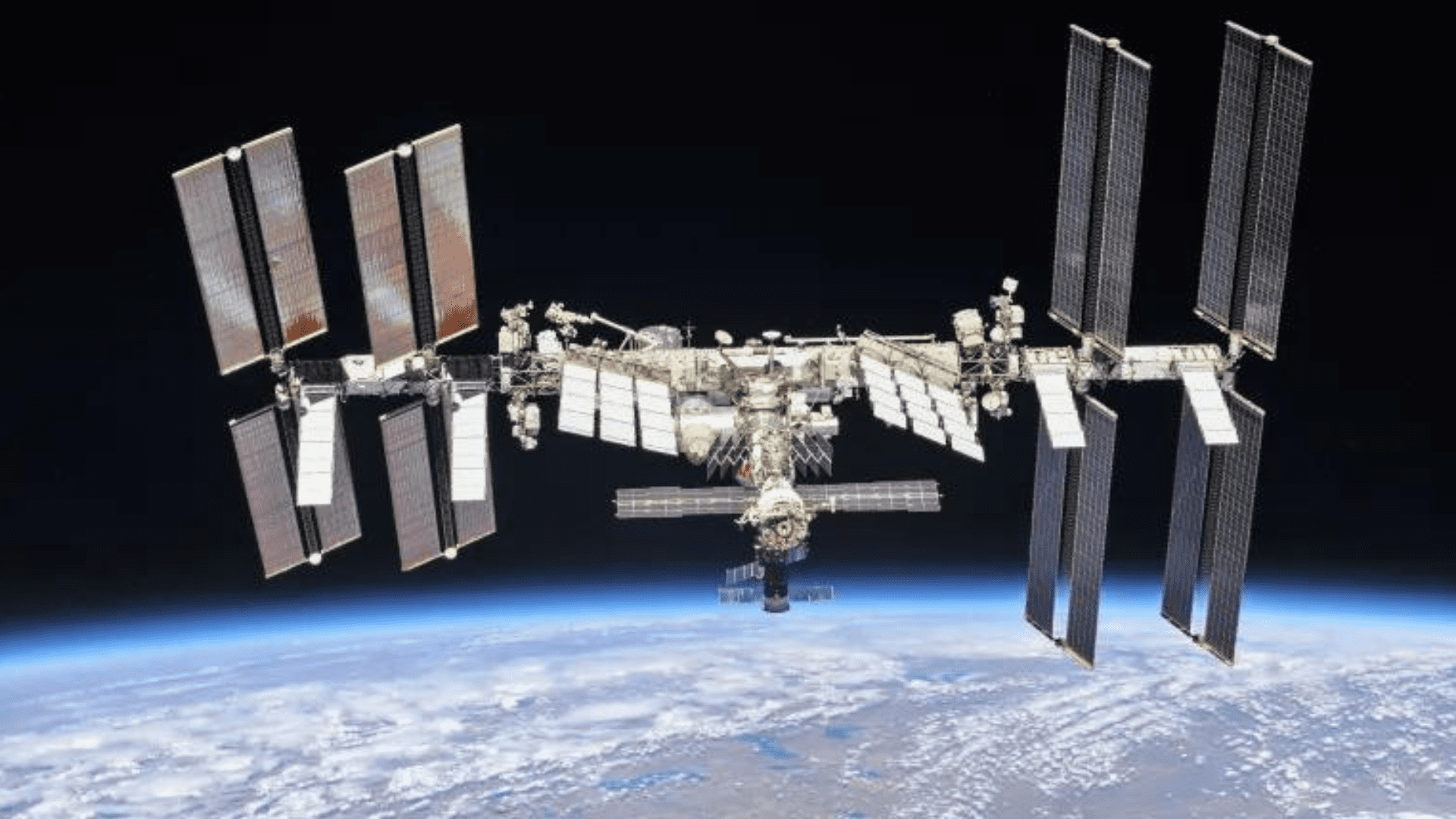
NASA is looking for a hub closer to home as The International Space Station’s lifespan inches closer to the end of its operational life. While they figure that out, they recently announced that Elon Musk’s SpaceX will be responsible for deorbiting the ISS.
Deorbiting the International Space Station
The International Space Station’s end of operational life is set for 2030. According to NASA, “It is crucial to prepare for the safe and responsible deorbit of the International Space Station in a controlled manner.” SpaceX is now responsible for developing and deploying the U.S. Deorbit Vehicle. This vehicle’s duty is to safely deorbit the space station and ensure avoidance of risk to populated areas.
Ken Bowersox is an associate administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate with NASA. He said, “Selecting a U.S. Deorbit Vehicle for the International Space Station will help NASA and its international partners ensure a safe and responsible transition in low Earth orbit at the end of station operations.” Despite pivoting to commercially owned destinations, the decision aligns with their future plans. Bowersox said, “This decision also supports NASA’s plans for future commercial destinations and allows for the continued use of space near Earth.”
NASA says that despite SpaceX’s development duties, the space agency is responsible for the mission’s ownership and operation. The vehicle will burn up in re-entry along with the ISS.
Explore Tomorrow's World from your inbox
Get the latest science, technology, and sustainability content delivered to your inbox.
I understand that by providing my email address, I agree to receive emails from Tomorrow's World Today. I understand that I may opt out of receiving such communications at any time.
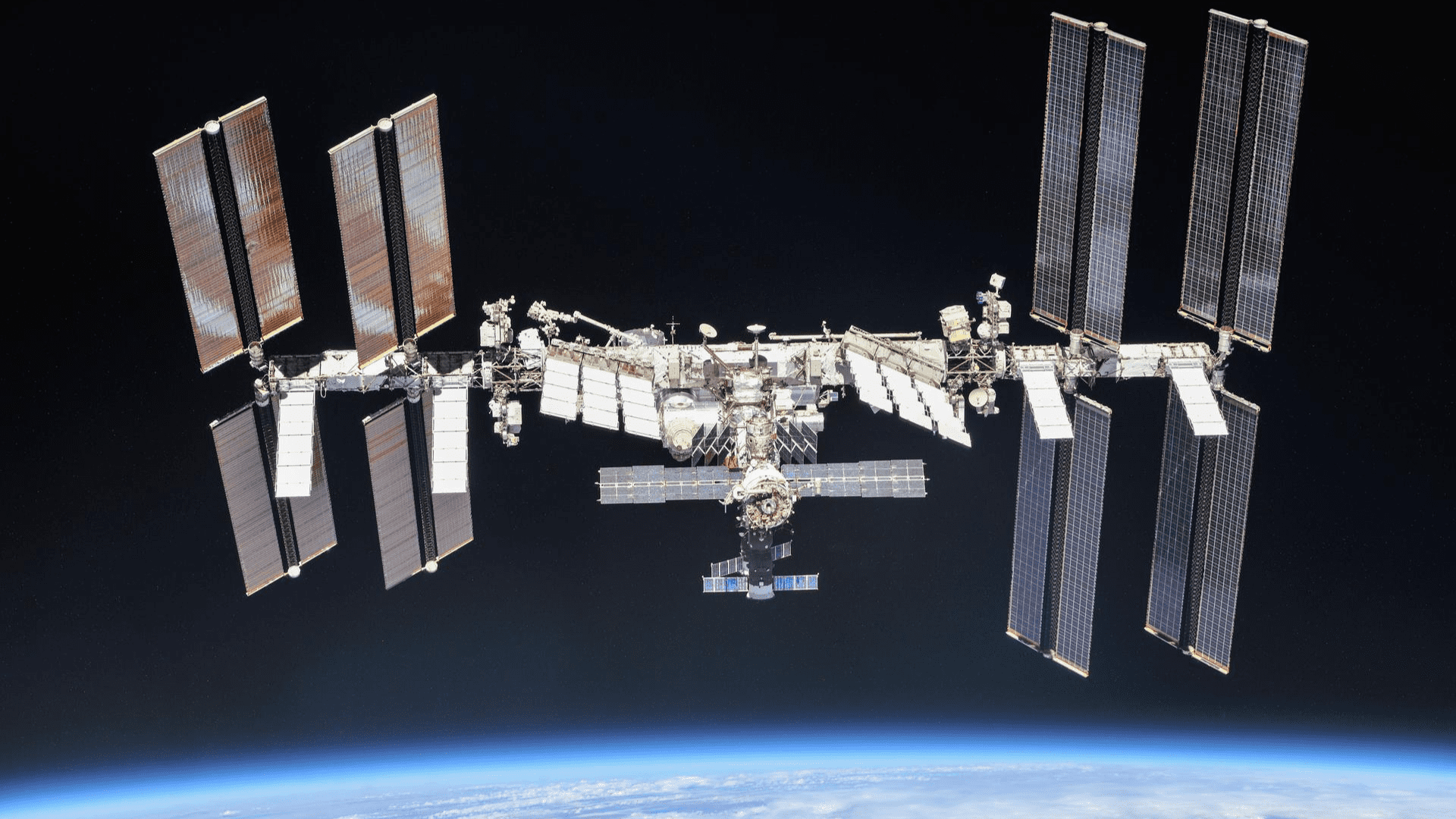
The Space Station
Since 1998, five space agencies have operated on the ISS. Including Canada’s space agency, the European Space Agency, Japan’s agency, NASA, and State Space Corporation Roscosmos. Each agency operating on the International Space Station is responsible for managing and operating the hardware they provide. The United States, Japan, Canada, and the participating countries of ESA are committed to operating through 2030. Russia is committed through at least 2028. However, all five space agencies are responsible for the safe deorbit of the ISS.
According to NASA, “the single-award contract has a total potential value of $843 million.”
In a statement, NASA said, “In its 24th year of continuously crewed operations, the space station is a unique scientific platform where crew members conduct experiments across multiple disciplines of research, including Earth and space science, biology, human physiology, physical sciences, and technology demonstrations not possible on Earth.”
Thousands of researchers have played a part in over 3,000 experiments in microgravity.