From new advancements in renewable energy to groundbreaking storage solutions, here are some of the latest innovations in clean energy.
Solar Energy
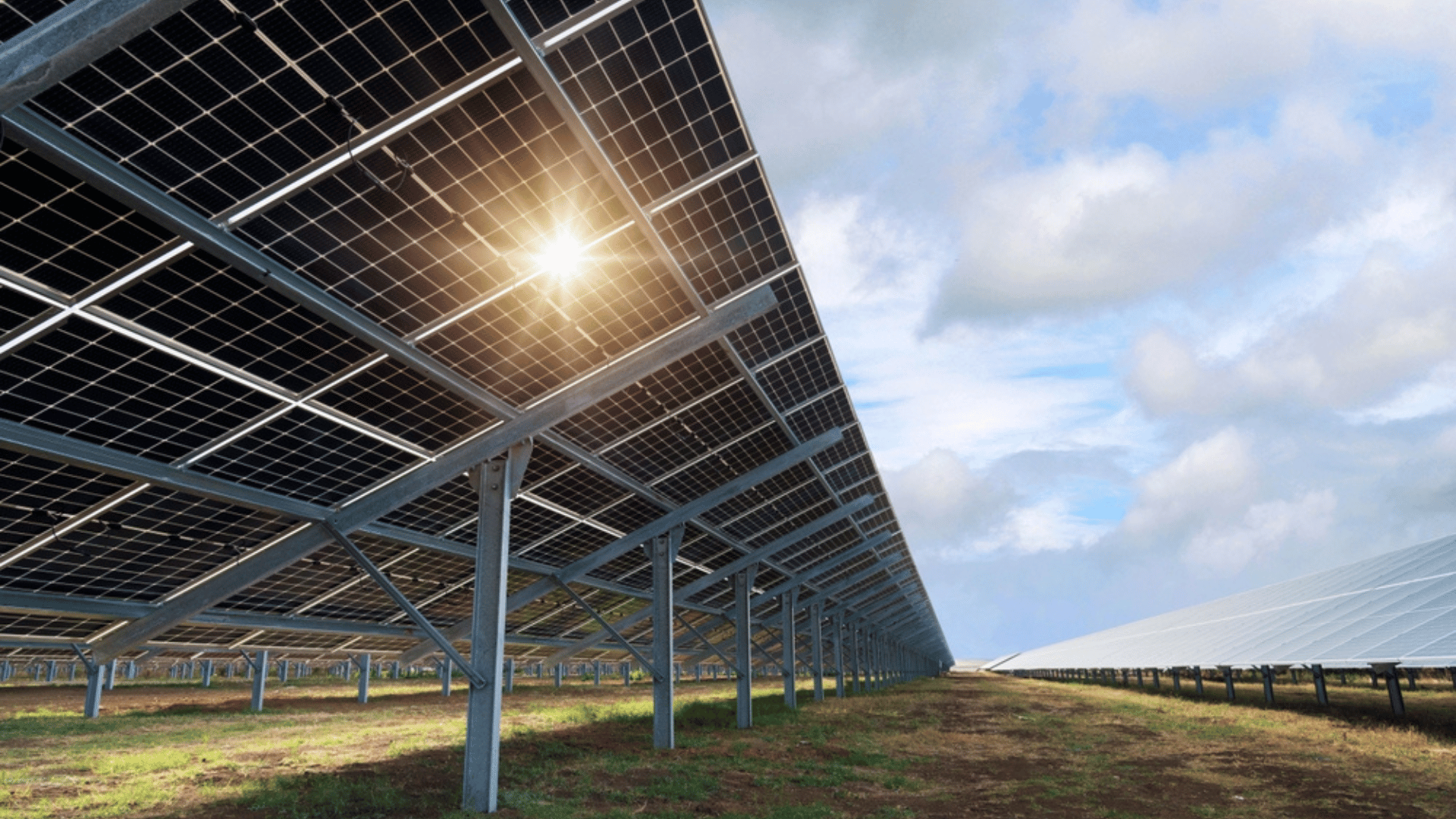
One of the current advances in solar panel technology is the introduction of more bifacial solar panel models instead of the widely used monofacial models. Monofacial solar panels have cells that only capture sunlight on the front side of the panel. In contrast, bifacial models have cells on both sides that allow them to capture both direct sunlight and reflected light from the ground or nearby surfaces.
In addition to bifacial models, companies such as Consumers Energy are also installing more single-axis tracking solar panels rather than traditional fixed panel models. Single-axis trackers are panels capable of moving and adjusting angles throughout the day to maximize sun exposure and increase energy efficiency.
Renewable Natural Gas
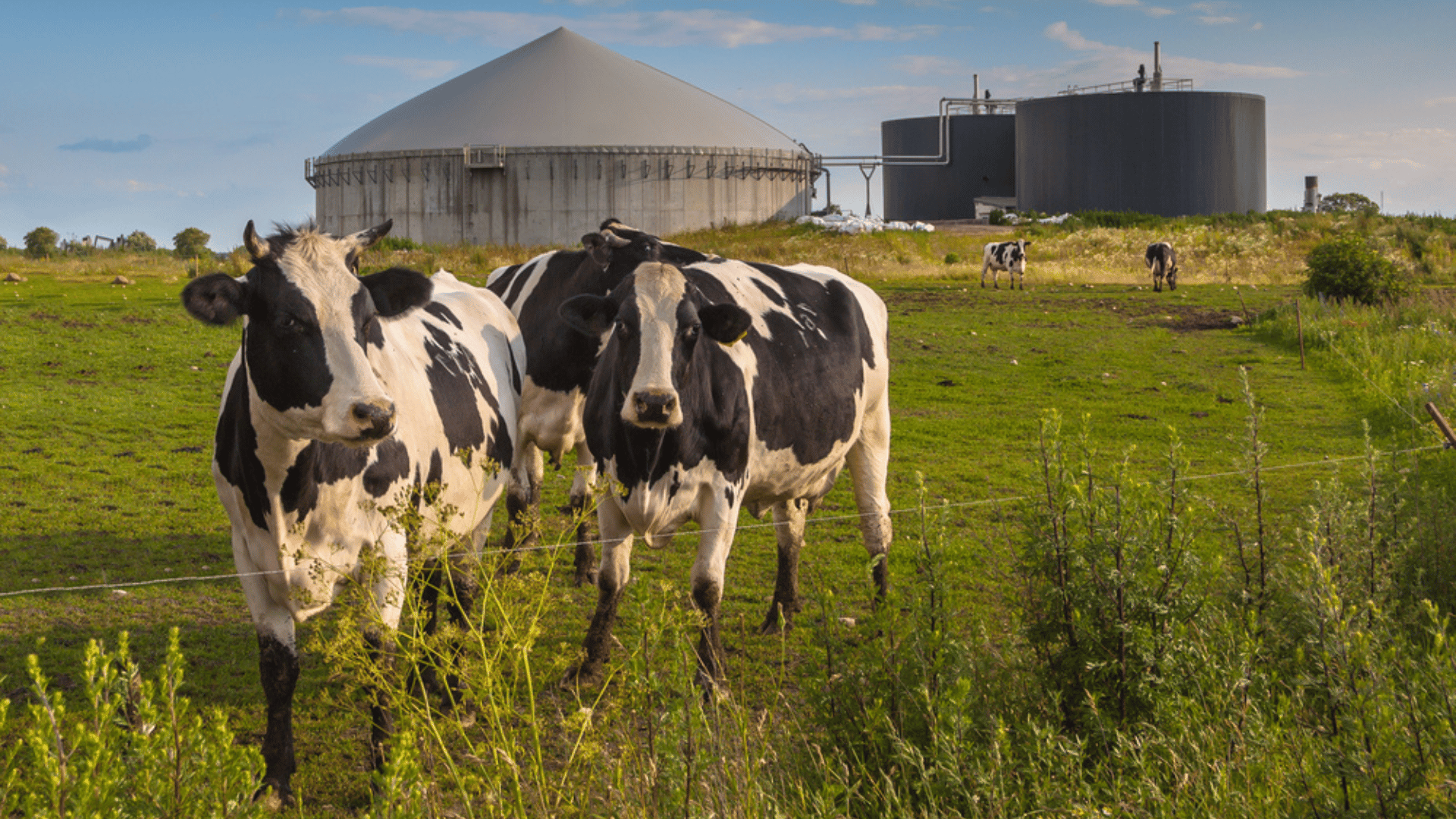

Renewable natural gas aims to turn something harming the environment into a green energy source. Methane, which cows naturally produce as a byproduct of their digestion, is released into the atmosphere and causes harm to the atmosphere. This gas, however, can also be collected and processed to generate electricity, heat, or even fuel for vehicles.
Otherwise known as biomethane, this gas is chemically identical to methane gas excavated from the Earth. Energy companies are, therefore, beginning to collaborate with dairy farmers in an effort to support the agricultural industry while safely obtaining this energy resource. Consumers Energy, for example, is building a 140 mega-watt solar facility called Spring Creek with Spring Creek Dairy Farm next door.
Hydroelectric Energy
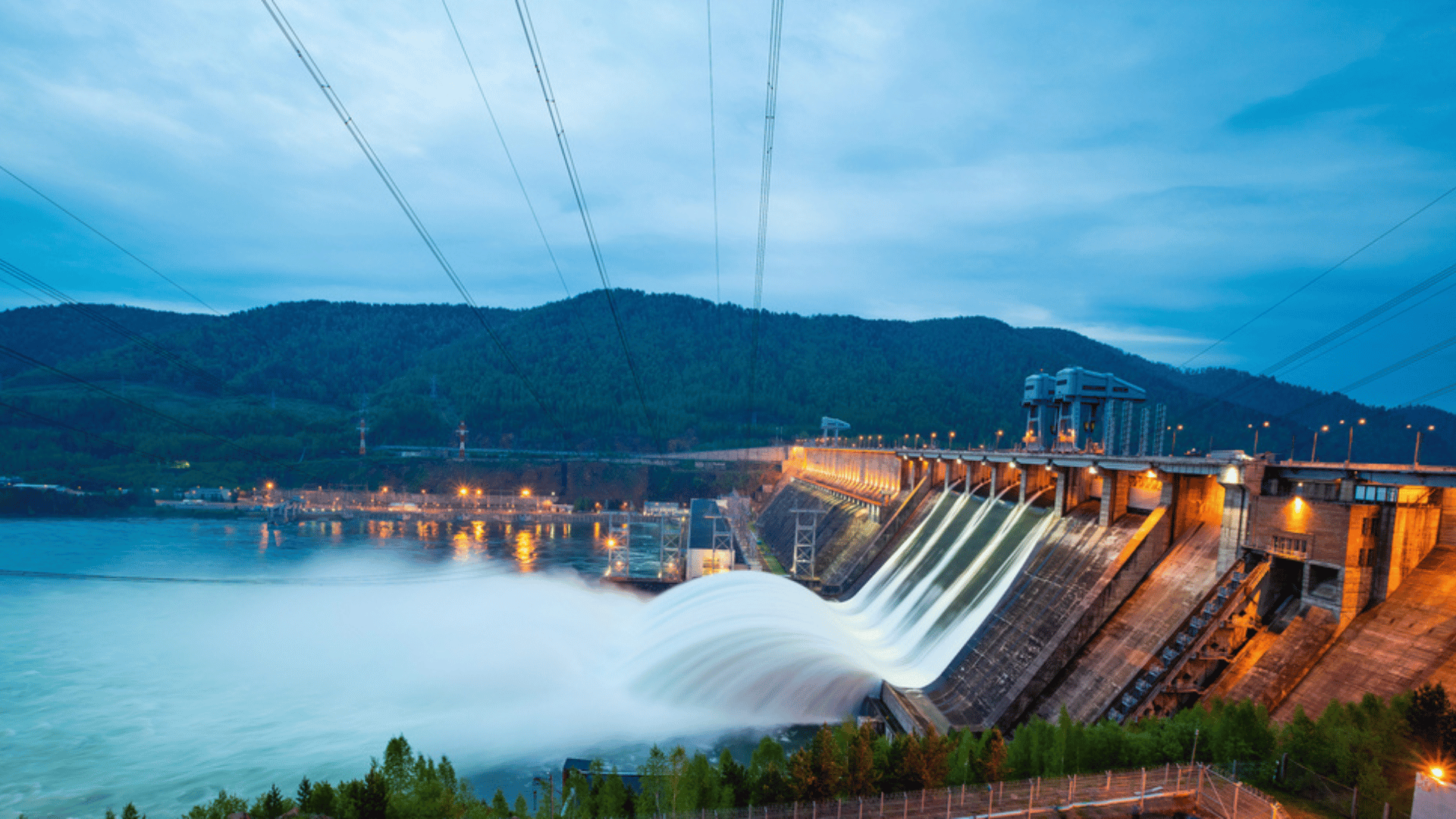

More companies are also working with hydroelectric energy, which harnesses the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. For example, the Ludington Pumped Storage Facility is located in Lake Michigan and is owned by both Consumers Energy and DTE Energy.
When their solar facilities are producing an excess of power, it’s used to power reversible pumps that pull water uphill and store it in a large reservoir. Then, when electric demand increases, the water is released from the 360-foot-high upper reservoir through a turbine generator to generate renewable electricity.
Tune in to Science Channel to watch Energy Transfer at 10 AM EST on Saturday, December 14!







