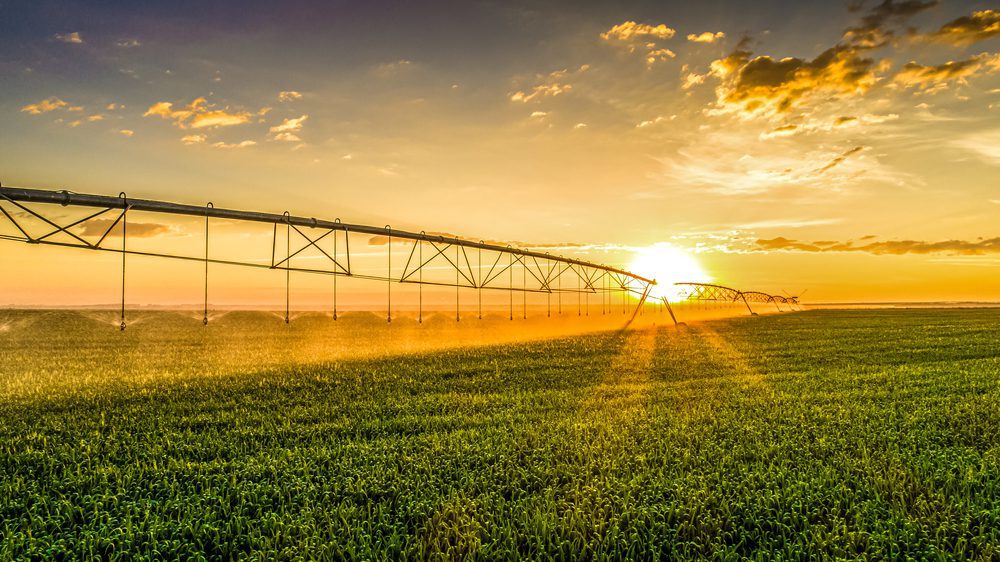
Wheat, bread, fruits, and vegetables are staples around the dinner table. We couldn’t imagine a world without them. But if it wasn’t for fertilizers, the farms we get food from couldn’t give us the produce we love. A good chunk of the phosphate that is used in the fertilizers farmers use to grow crops in North America comes from The Mosaic Company’s mines in Florida. The world relies on Florida phosphate to help the world grow the food it needs.
Phosphate to Farming

According to Mosaic, its mines make nearly half of the phosphate-based crop nutrients in North America. Mosaic is the world’s leading integrated producer of phosphate and potash. Phosphate is mined in Florida and transported by trucks or rail to manufacturing facilities. This is where the phosphate rock is turned into Mosaic’s fertilizer products.
The Mosaic Company’s products account for 73 percent of North America’s annual phosphate production. However, mining and production are the start of a global effort to address food insecurity.
Phosphate, Farming, and Feeding
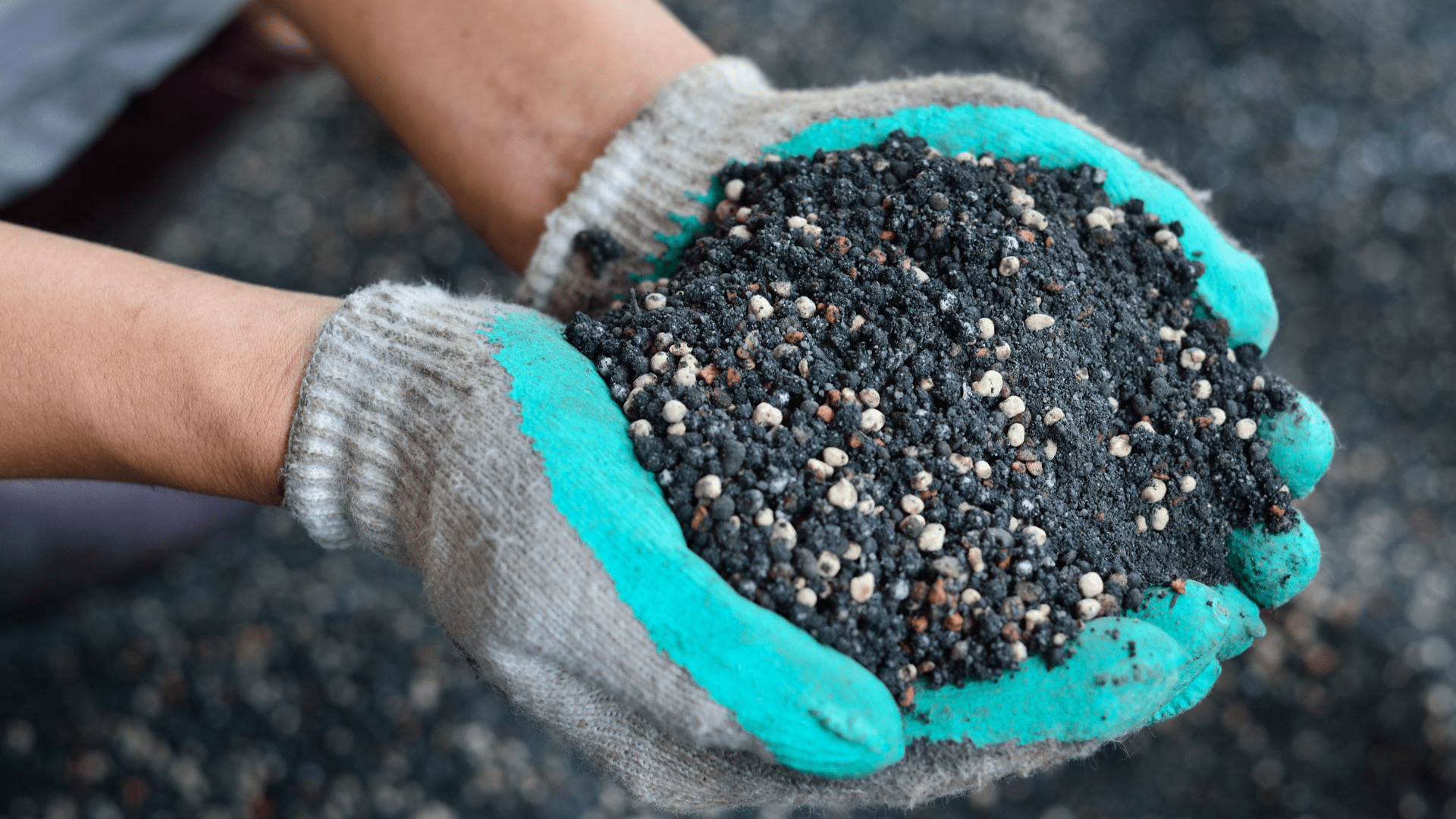

Because of phosphate and potash, farmers can grow the crops that end up in our pantries and on the dinner table.
From the cornfields in Nebraska and Iowa to the waves of wheat in Kansas and all the way to the soybeans in Illinois, Florida phosphate is the unsung hero of bountiful harvests. Annually, Mosaic’s Supply Chain team moves 460,000 trucks, 305,000 railcars, 1,800 river barges, 500 vessels, and 2,000 containers filled with phosphate. Much of it goes to the farmers in America’s heartland.
According to Mosaic, there is no substitute for phosphate. Additionally, crop yields are 10 to 30 percent higher using phosphate-based nutrients. But what does phosphate do that makes it so critical? There are several things. For example, the nutrient stimulates root development. Its powers extend to increased stalk and stem strength. In addition, it improves flower formation and seed production. Phosphate increases resistance to diseases and helps development throughout a crop’s life cycle.
Explore Tomorrow's World from your inbox
Get the latest science, technology, and sustainability content delivered to your inbox.
I understand that by providing my email address, I agree to receive emails from Tomorrow's World Today. I understand that I may opt out of receiving such communications at any time.
Sustainable Life Cycle
Potash and Phosphate have a few things in common. They are both natural and concentrated in deposits resulting from pre-historic life on earth. Recoverable deposits of potash and phosphate are not found everywhere but are limited to several distinct places worldwide.
In addition to manufacturing critical crop nutrients that will play a key role in helping feed roughly 9 billion people by 2050, Mosaic has an agronomy team that works with farmers to help them optimize the use of these products for maximum yield using best practices to protect the environment.
Educating
The 4R Nutrient Stewardship Program is a framework that encourages farmers to apply the right fertilizer at the right rate, at the right time, and in the right place. Not only does this yield better results for farmers, it also lessens the impact on the environment and can even help curb the effects of climate change.
The goal behind all of this is simple… Help farmers grow more food, on less land while working to help feed billions of people across the globe.
“With more than 13,000 employees, we serve customers in more than 40 countries and have implemented 4R Nutrient Stewardship practices on more than 6 million acres in North America,” said Sarah Fedorchuk, Mosaic Vice President of Public Affairs and Government Relations.
Tune in to the Science Channel to watch Digging For Dinner at 10 AM on Saturday, May 11!